Since Tizen 2.4
Route API provides a routing path from an origin to a destination.
Route API is one of the Maps Services provided by the Tizen Native Location Framework.
To start using the Route API we are going to:
- Create an empty Tizen native application.
- Start the Maps Service.
- Run a route request.
This document assumes that you already have basic knowledge in Tizen development. For basic information, see https://developer.tizen.org/development/getting-started/preface
The Maps Service API requires a security key issued by the maps provider.
In case of HERE maps, the security key is a concatenation of app_id and app_code, generated on https://developer.here.com/plans/api/consumer-mapping according to your consumer plan.
“your-security-key” is “app_id/app_code”
Note: Make sure your device or emulator has a valid internet connection.
To ensure the Maps Service API execution, set the following privileges:
- http://tizen.org/privilege/mapservice
- http://tizen.org/privilege/internet
- http://tizen.org/privilege/network.get
In the IDE, create an empty application using the basic UI application template, and run it on an emulator or a device.
The "Hello Tizen" label appears on the screen at application startup.
NOTE: Get familiar with instructions on how to create an empty application at https://developer.tizen.org/development/getting-started/native-application/creating-your-first-tizen-application.
#include <maps_service.h>NOTE: This inclusion allows you to use all native Maps Service API functions and features. For more details, see https://developer.tizen.org/development/api-references/, and go to 2.4 API References -> Native Application -> Mobile Native -> Native API Reference -> Location -> Maps Service.
typedef struct appdata {
Evas_Object *win;
Evas_Object *conform;
Evas_Object *label;
maps_service_h maps; // Maps Service handle
} appdata_s;static bool
app_create(void *data)
{
appdata_s *ad = data;
create_base_gui(ad);
// Specify the maps provider name
if (maps_service_create("HERE", &ad->maps) != MAPS_ERROR_NONE)
return false;
// Set the security key issued by the maps provider
maps_service_set_provider_key(ad->maps, "your-security-key");
return true;
}static void
app_terminate(void *data)
{
// Release all resources
appdata_s *ad = data;
maps_service_destroy(ad->maps);
}To run a route request:
int request_id = 0;
maps_coordinates_h origin = NULL, destination = NULL;
maps_coordinates_create(50.0734902, 14.4279653, &origin);
maps_coordinates_create(50.0860608, 14.4145915, &destination);
// Use the Route API
maps_service_search_route(ad->maps, origin, destination, NULL, search_route_cb, ad, &request_id);After creating the request, release any temporary data:
maps_coordinates_destroy(origin);
maps_coordinates_destroy(destination);static bool
search_route_cb(maps_error_e error, int request_id, int index, int total,
maps_route_h route, void* user_data)
{
double distance = .0;
long duration = 0;
char route_info[0x100] = {0};
maps_route_get_total_distance(route, &distance);
maps_route_get_total_duration(route, &duration);
snprintf(route_info, 0x100, "Route duration %.0f min, length %.3f km",
ceil(1. * duration / 60), distance / 1000);
appdata_s *ad = user_data;
elm_object_text_set(ad->label, route_info);
// Release the route handle
maps_route_destroy(route);
// If return true, you receive other routes,
// corresponding to the search parameters
// In this example, 1 route is enough
return true;
}At first, the familiar "Hello Tizen" line appears. A moment later, however, it changes to "Route duration 9 min, length 2.889 km". This indicates the calculated route from a Prague pub to the Karluv Most bridge.
To use route maneuvers:
static bool
app_create(void *data)
{
// Hook to take necessary actions before main event loop starts
// Initialize UI resources and application data
// If this function returns true, the main loop of application starts
// If this function returns false, the application is terminated
appdata_s *ad = data;
create_base_gui(ad);
// Specify the maps provider name
if (maps_service_create("HERE", &ad->maps) != MAPS_ERROR_NONE)
return false;
// Set the security key issued by the maps provider
maps_service_set_provider_key(ad->maps, "your-security-key");
// Set distance units
maps_preference_h preference = NULL;
maps_preference_create(&preference);
maps_preference_set_distance_unit(preference, MAPS_DISTANCE_UNIT_M);
int request_id = 0;
maps_coordinates_h origin = NULL, destination = NULL;
maps_coordinates_create(50.0734902, 14.4279653, &origin);
maps_coordinates_create(50.0860608,14.4145915, &destination);
// Use the Route API
maps_service_search_route(ad->maps, origin, destination, preference, search_route_cb, ad, &request_id);
maps_coordinates_destroy(origin);
maps_coordinates_destroy(destination);
maps_preference_destroy(preference);
return true;
}2. To iterate through the segment and maneuver lists of the route, modify the search_route_cb() function as follows:
static bool
search_route_cb(maps_error_e error, int request_id, int index, int total,
maps_route_h route, void* user_data)
{
double distance = .0;
long duration = 0;
char route_info[0x1000] = {0};
maps_route_get_total_distance(route, &distance);
maps_route_get_total_duration(route, &duration);
snprintf(route_info, 0x1000, "Route duration %.0f min, length %.3f km",
ceil(1. * duration / 60), distance / 1000);
// Bonus: print list of maneuvers to reach the destination
maps_route_foreach_segment(route, route_segment_cb, route_info);
appdata_s *ad = user_data;
elm_object_text_set(ad->label, route_info);
// Release the route handle
maps_route_destroy(route);
// If return true, you receive other routes,
// corresponding to the search parameters
// In this example, 1 route is enough
return true;
}static bool
route_segment_maneuver_cb(int index, int total, maps_route_maneuver_h maneuver, void *user_data)
{
char *route_info = (char *)user_data;
char *instruction_text = NULL;
const int max_line_len = 64;
const int half_line_len = max_line_len / 2;
char num[0x10] = {0};
maps_route_maneuver_get_instruction_text(maneuver, &instruction_text);
if (instruction_text && strlen(instruction_text))
{
// Add the instruction number
snprintf(num, 0x10, " %d: ", index + 1);
strcat(route_info, num);
// Add the instruction text
const int l = strlen(instruction_text);
if (l > max_line_len)
{ // If the instruction is too long, extract the middle part
// Add the first part of the instruction
char instruction_head[half_line_len + 1] = {0};
snprintf(instruction_head, half_line_len - 3, "%s", instruction_text);
strcat(route_info, instruction_head);
// Add the first and second part separator
strcat(route_info, "...");
// Add the second part of the instruction
char instruction_tail[half_line_len + 1] = {0};
snprintf(instruction_tail, half_line_len, "%s", instruction_text + l - half_line_len);
strcat(route_info, instruction_tail);
}
else
// Add whole instruction
strcat(route_info, instruction_text);
}
free(instruction_text);
maps_route_maneuver_destroy(maneuver);
return true;
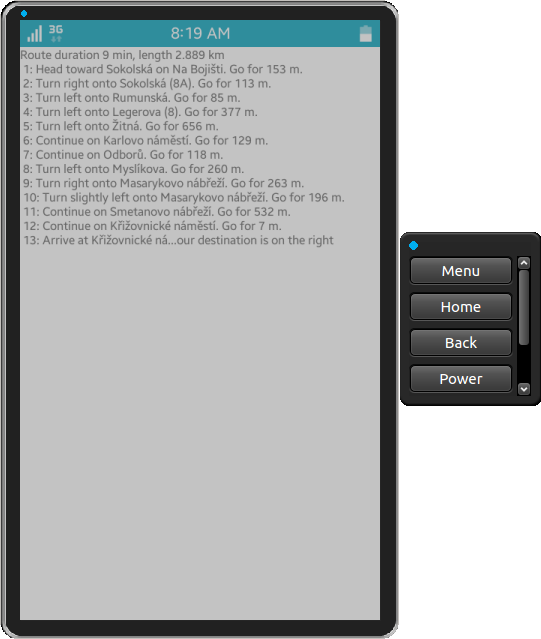
}A moment after startup, the application shows the familiar route information and a list of 13 maneuvers required to get from the specified origin to the destination.
https://developer.tizen.org/community/tip-tech/how-use-tizen-native-route-api-3-steps