| subcategory |
|---|
AWS |
-> Note This resource has an evolving API, which will change in the upcoming versions of the provider in order to simplify user experience.
This resource allows you to set up workspaces in E2 architecture on AWS. Please follow this complete runnable example with new VPC and new workspace setup.
To get workspace running, you have to configure a couple of things:
- databricks_mws_credentials - You can share a credentials (cross-account IAM role) configuration ID with multiple workspaces. It is not required to create a new one for each workspace.
- databricks_mws_storage_configurations - You can share a root S3 bucket with multiple workspaces in a single account. You do not have to create new ones for each workspace. If you share a root S3 bucket for multiple workspaces in an account, data on the root S3 bucket is partitioned into separate directories by workspace.
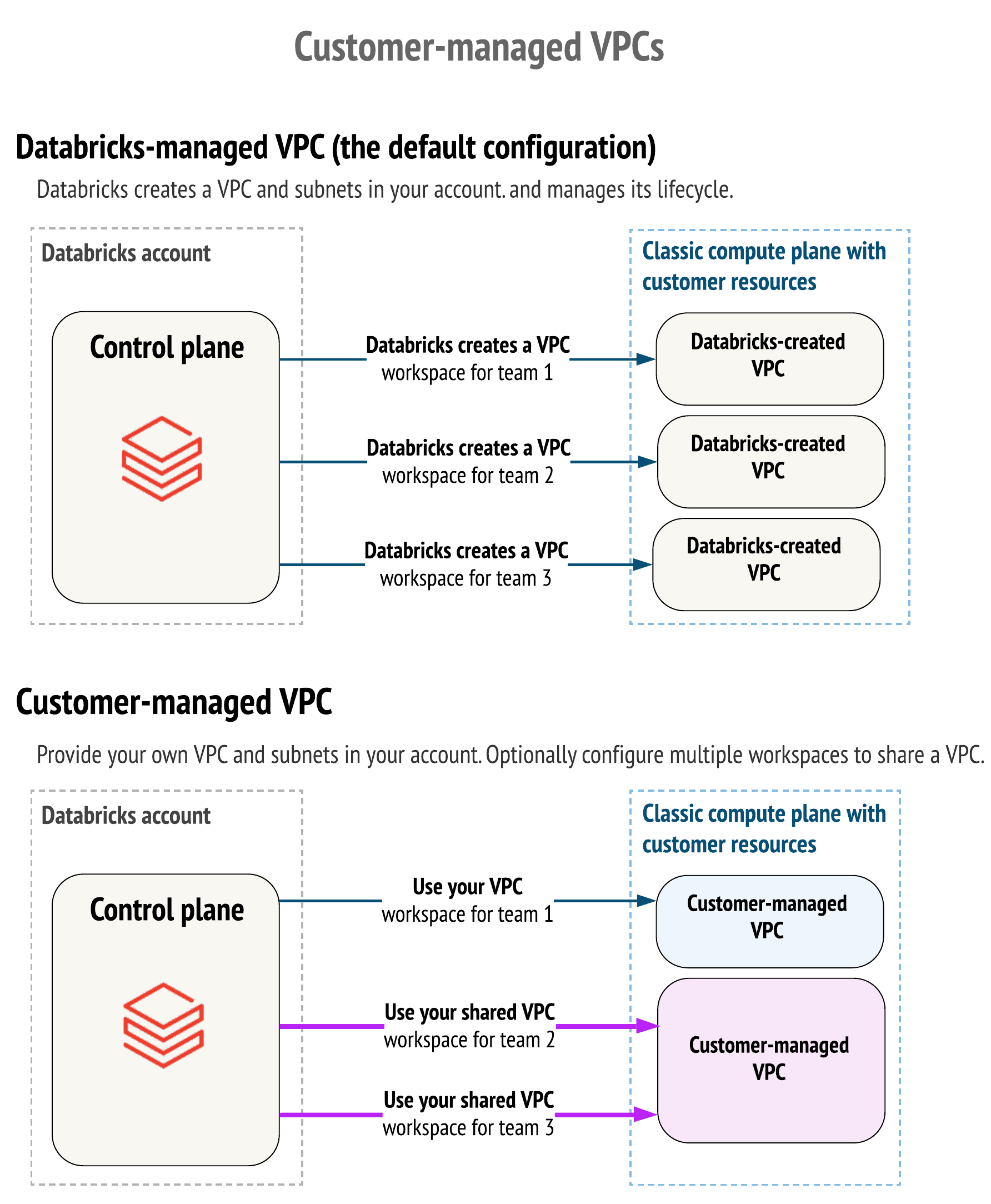
- databricks_mws_networks - (optional, but recommended) You can share one customer-managed VPC with multiple workspaces in a single account. You do not have to create a new VPC for each workspace. However, you cannot reuse subnets or security groups with other resources, including other workspaces or non-Databricks resources. If you plan to share one VPC with multiple workspaces, be sure to size your VPC and subnets accordingly. Because a Databricks databricks_mws_networks encapsulates this information, you cannot reuse it across workspaces.
- databricks_mws_customer_managed_keys - You can share a customer-managed key across workspaces.
variable "databricks_account_id" {
description = "Account Id that could be found in the bottom left corner of https://accounts.cloud.databricks.com/"
}
provider "databricks" {
alias = "mws"
host = "https://accounts.cloud.databricks.com"
}
// register cross-account ARN
resource "databricks_mws_credentials" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
credentials_name = "${var.prefix}-creds"
role_arn = var.crossaccount_arn
}
// register root bucket
resource "databricks_mws_storage_configurations" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
storage_configuration_name = "${var.prefix}-storage"
bucket_name = var.root_bucket
}
// register VPC
resource "databricks_mws_networks" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
network_name = "${var.prefix}-network"
vpc_id = var.vpc_id
subnet_ids = var.subnets_private
security_group_ids = [var.security_group]
}
// create workspace in given VPC with DBFS on root bucket
resource "databricks_mws_workspaces" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
workspace_name = var.prefix
deployment_name = var.prefix
aws_region = var.region
credentials_id = databricks_mws_credentials.this.credentials_id
storage_configuration_id = databricks_mws_storage_configurations.this.storage_configuration_id
network_id = databricks_mws_networks.this.network_id
}
provider "databricks" {
// in normal scenario you won't have to give providers aliases
alias = "created_workspace"
host = databricks_mws_workspaces.this.workspace_url
}
// create PAT token to provision entities within workspace
resource "databricks_token" "pat" {
provider = databricks.created_workspace
comment = "Terraform Provisioning"
// 1 day token
lifetime_seconds = 86400
}By default, Databricks creates a VPC in your AWS account for each workspace. Databricks uses it for running clusters in the workspace. Optionally, you can use your VPC for the workspace, using the feature customer-managed VPC. Databricks recommends that you provide your VPC with databricks_mws_networks so that you can configure it according to your organization’s enterprise cloud standards while still conforming to Databricks requirements. You cannot migrate an existing workspace to your VPC. Please see the difference described through IAM policy actions on this page.
variable "databricks_account_id" {
description = "Account Id that could be found in the bottom left corner of https://accounts.cloud.databricks.com/"
}
resource "random_string" "naming" {
special = false
upper = false
length = 6
}
locals {
prefix = "dltp${random_string.naming.result}"
}
data "databricks_aws_assume_role_policy" "this" {
external_id = var.databricks_account_id
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "cross_account_role" {
name = "${local.prefix}-crossaccount"
assume_role_policy = data.databricks_aws_assume_role_policy.this.json
tags = var.tags
}
data "databricks_aws_crossaccount_policy" "this" {
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy" "this" {
name = "${local.prefix}-policy"
role = aws_iam_role.cross_account_role.id
policy = data.databricks_aws_crossaccount_policy.this.json
}
resource "databricks_mws_credentials" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
credentials_name = "${local.prefix}-creds"
role_arn = aws_iam_role.cross_account_role.arn
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "root_storage_bucket" {
bucket = "${local.prefix}-rootbucket"
acl = "private"
versioning {
enabled = false
}
force_destroy = true
tags = var.tags
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_public_access_block" "root_storage_bucket" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.id
ignore_public_acls = true
}
data "databricks_aws_bucket_policy" "this" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.bucket
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_policy" "root_bucket_policy" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.id
policy = data.databricks_aws_bucket_policy.this.json
}
resource "databricks_mws_storage_configurations" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
storage_configuration_name = "${local.prefix}-storage"
bucket_name = aws_s3_bucket.root_storage_bucket.bucket
}
resource "databricks_mws_workspaces" "this" {
provider = databricks.mws
account_id = var.databricks_account_id
workspace_name = local.prefix
deployment_name = local.prefix
aws_region = "us-east-1"
credentials_id = databricks_mws_credentials.this.credentials_id
storage_configuration_id = databricks_mws_storage_configurations.this.storage_configuration_id
}In order to create a Databricks Workspace that leverages AWS PrivateLink please ensure that you have read and understood the Enable Private Link documentation and then customise the example above with the relevant examples from mws_vpc_endpoint, mws_private_access_settings and mws_networks.
-> Note All workspaces would be verified to get into runnable state or deleted upon failure. You can only update credentials_id, network_id, and storage_customer_managed_key_id on a running workspace.
The following arguments are available and cannot be changed after workspace is created:
account_id- Account Id that could be found in the bottom left corner of Accounts Console.managed_services_customer_managed_key_id- (Optional)customer_managed_key_idfrom customer managed keys withuse_casesset toMANAGED_SERVICES. This is used to encrypt the workspace's notebook and secret data in the control plane.deployment_name- (Optional) part of URL:https://<deployment-name>.cloud.databricks.comworkspace_name- name of the workspace, will appear on UIaws_region- AWS region of VPCstorage_configuration_id-storage_configuration_idfrom storage configurationprivate_access_settings_id- (Optional) Canonical unique identifier of databricks_mws_private_access_settings in Databricks Account
The following arguments could be modified after the workspace is running:
network_id- (Optional)network_idfrom networks. Modifying networks on running workspaces would require three separateterraform applysteps.credentials_id-credentials_idfrom credentialsstorage_customer_managed_key_id- (Optional)customer_managed_key_idfrom customer managed keys withuse_casesset toSTORAGE. This is used to encrypt the DBFS Storage & Cluster EBS Volumes.
In addition to all arguments above, the following attributes are exported:
id- Canonical unique identifier for the workspace.workspace_status_message- (String) updates on workspace statusworkspace_status- (String) workspace statuscreation_time- (Integer) time when workspace was createdworkspace_url- (String) URL of the workspace
The timeouts block allows you to specify create, read and update timeouts. It usually takes 5-7 minutes to provision Databricks E2 Workspace and another couple of minutes for your local DNS caches to resolve. Please launch TF_LOG=DEBUG terraform apply whenever you observe timeout issues.
timeouts {
create = "30m"
read = "10m"
update = "20m
}You can reset local DNS caches before provisioning new workspaces with one of the following commands:
- Linux -
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart - Mac OS Sierra, X El Capitan, X Mavericks, X Mountain Lion, or X Lion -
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder - Mac OS X Yosemite -
sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches - Mac OS X Snow Leopard -
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache - Mac OS X Leopard and below -
sudo lookupd -flushcache